What Is Purpose-Driven Leadership?
As news headlines proliferate about what today’s employees want from work and how much organizations can expect from their people, purpose is emerging as a critical success factor. Purpose in leadership supports improved individual and organizational outcomes.
Purpose-driven leadership means helping employees find personal meaning in their work and fostering a deeply committed workforce that thrives on shared goals and aspirations. Purpose-driven leaders model value-based decision-making, take time to learn what truly matters to their employees, connect work to a greater objective, and help employees understand their organization’s mission and find ways to personally connect to it.
But purpose, just like organizational culture change, doesn’t thrive without intentional effort. To create a sustainable culture of purpose-driven leadership, managers must embody and promote a sense of purpose in their leadership, daily operations, and decision-making.
Why Is Purpose-Driven Leadership Important?
Understanding the Role of Purpose in Leadership
Purpose-driven leadership helps create a shared sense of direction, alignment, and commitment and fosters greater performance, persistence, and belonging at the organization. In fact, purpose is often one of the main drivers of employee engagement and satisfaction. Our research with emerging leaders around the globe suggests that purpose is one of the greatest predictors of whether young professionals pursue leadership positions and, for those in a leadership role, whether leaders feel empowered to make a difference. Purpose-driven leaders are more likely to develop and maintain strong relationships with their direct reports and are better equipped to navigate leadership challenges.
Articulating a clear, inspiring vision that resonates with direct reports and colleagues is key for purpose-driven leadership. Purpose-driven leaders also create space for alignment of goals and values between individual employees and the overall organization. When employees understand why they’re carrying out their work, they care more about what they accomplish.
Though critical for all employees, value alignment is especially key for younger generations in the workforce. At a time where Gen Z and Millennials are at the heart of the Great Reshuffling, organizational mission and vision can be an important deciding factor in recruitment and retention — especially among younger workers — in the post-pandemic world. Finding purpose in day-to-day work also helps employees persist, even through challenging tasks.
Purpose Is Universal, But Not Uniform
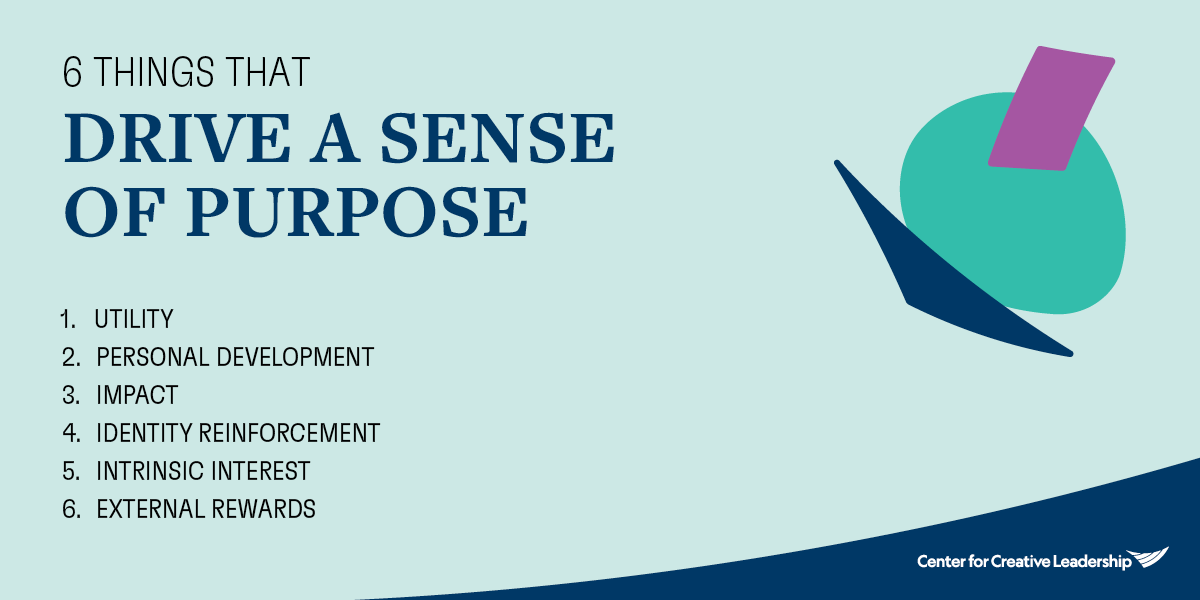
6 Things That Drive a Sense of Purpose
While the desire for purpose is a fundamental human need, what employees value is not. Research suggests that purpose can arise from a range of sources, such as:
- Utility: Work is practically relevant to our goals and aspirations, either now or in the future.
- Personal Development: Work facilitates opportunities for self-growth, developing either skillsets or mindsets in personally meaningful ways.
- Impact: Work empowers us to make a tangible and positive difference in the world, contributing to the greater good of society, our communities, or those close to us.
- Identity Reinforcement: Work reinforces our sense of self, aligning with the core elements of who we are.
- Intrinsic Interest: Work is inherently fun and energizing, offering enjoyable experiences that naturally appeal to our interests.
- External Rewards: Work leads to a desirable payoff, from a paycheck to a promotion.
As varied as the unique experiences that individuals bring to work are the ways they find meaning in it. Take, for instance, being asked to help start a new employee resource group at an organization. One person may jump at the opportunity because it helps display leadership potential (utility) and is accompanied by an additional stipend (external). Another might agree because they see themselves as someone who advocates for wellbeing (identity) and want to support work colleagues (prosocial). Both employees may be taking the same purpose-driven action, but they have different reasons for doing so. Without exploring their unique drivers, leaders simply cannot know why employees choose to engage at work.
Each Finding Their Own Meaning Is Critical
Why is it important to know what your employees value? Because telling them where to find meaning can backfire. In one study, researchers conducted a series of experiments teaching college students a new mental math technique. They found that telling students why the approach was valuable undermined how well they applied it and how interested they were in using it in the future. Importantly, this impacted the least confident students the most.
Consider a parallel at work. If a sales director tells his regional leads exactly why they should care about a new system for tracking leads, there’s a stronger chance that buy-in and performance will suffer if those reasons don’t personally matter to the employees. If employees have an opportunity to identify why the system is useful to them and make connections for themselves, by contrast, they’re likely to use the program more frequently and effectively. You want each person to be able to determine for themselves why and how their work connects to purpose, rather than dictating to them why it’ll be valuable. When your employees have autonomy to find their own meaning, a culture of purpose is easier to cultivate.
To be clear, this doesn’t imply that leaders should avoid sharing their own reasons why work is meaningful. Modeling conversations about purposeful leadership can help employees find their own meanings. The critical piece is to allow individuals the freedom and permission to consider and discuss their own purpose, so their reasons feel relevant and personal to them.
Implementing Purpose-Driven Leadership at Your Organization
2 Keys for Cultivating Greater Purpose in Leadership
It’s one thing to say that purpose is important, and another to create a culture of purpose-driven leadership at your organization. While few people disagree that purpose in leadership is important, it’s not ubiquitous. If leading with purpose was easy or intuitive, everyone would be doing it.
So, how can managers embrace and embody purpose in leadership and their everyday work? Here are 2 essential keys to cultivating an environment where managers and employees can connect and find purpose in leadership and in their daily work.
1. Weave Organizational Mission, Vision & Values Into Your Communications.
Remember that employees have to know the organization’s overarching purpose before they can make connections to it for themselves. Values may drive your organization’s decision-making at the most senior levels, but they’re easy for employees to overlook in the midst of projects, deadlines, and day-to-day activities. So, it’s important to speak often about your organization’s mission, vision, and values to give employees ample opportunities to connect and align their own values to their tasks and projects.
Make purpose more salient for them by effectively and intentionally communicating the vision, mission, and values of the organization — and by reinforcing these again and again over time.
To try more purpose-driven leadership: Model finding connections between organizational values and your team’s (or your own) projects whenever possible. Some specific practices to try:
- Seek out opportunities to build purpose alignment into existing structures at work, such as during annual reviews or all-staff meetings. Invite your senior leadership team to provide examples of leading with purpose (both personal and organizational) in public settings, company-wide communications, quarterly retreats, and team meetings. Personal, specific, and meaningful stories are most effective at signaling a commitment to purpose and catalyzing greater buy-in and alignment. Make a point of bringing powerful real-life experiences to the forefront; sharing examples of helping others or bettering a community at large through corporate social responsibility efforts can be particularly helpful.
- Consider asking colleagues directly what parts of the organizational mission resonate most for each of them. You can open the door for deeper exploration by modeling; simply take 5 minutes to think about or list your personal values, current work activities, and note the specific, meaningful connections you see between them. Share as much of this as you like and use it as a discussion-starter to learn more about what matters most to others. When new employees onboard or move into bigger roles, intentionally engage them in team meetings or one-on-one conversations about how their work might fit into the bigger organizational picture.
- At the beginning and/or end of projects, build in time for team members to reflect on how the project contributes to the organization’s overall business objectives and mission. This can be part of the conversations for setting team norms up front, or used as an exercise during an after-action review or “lessons learned” session after the fact.
When weaving organizational purpose and mission into conversations, remember that employees need dedicated time to reflect on the connections for themselves. By building in intentional opportunities to find meaning, purpose-driven leaders signal to employees that finding purpose at work is a valued part of the organizational culture.
Access Our Webinar!
Watch our webinar, Why Organizations Should Encourage Leadership Purpose, to learn how managers who help their teams find personal meaning and connection foster purpose-driven leadership, leading to increased productivity, employee engagement, and retention.
2. Understand What Drives Your Team Members.
The more you know your employees — and create opportunities for them to connect with one another and the larger organization — the easier it is to help reinforce their sense of purpose. Seek to understand the perspectives of your direct reports through a lens of showing compassion and respect for their diverse identities, as each individual brings a different set of experiences and aspirations to work.
Compassionate leadership means being aware of the feelings, thoughts, and needs of others. Compassion enables leaders to understand and respond to the unique needs, perspectives, and emotions of their teams, fostering a more supportive and inclusive environment. Beyond the obvious feel-good value of showing compassion, our researchers have found that managers who practice empathy toward those they are responsible for are viewed as better performers by their bosses. It’s a “win” for all involved.
Purpose-driven leaders also understand and leverage the power of identity. This involves both creating an environment where team members feel psychologically safe at work to share their personal experiences and understanding the way that employees view themselves with respect to work. For instance, our research suggests that simply identifying as a leader is associated with greater confidence and engagement in the workplace and can be cultivated by support from others.
To try more purpose-driven leadership: Help employees recognize and embrace the many different reasons they might find meaning at work. Some specific practices to try:
- Share your own reasons that you find your work meaningful, providing examples of several different sources of purpose. Speak in the first person (using I, we, my, our, etc.), and encourage them to do the same. Include details and examples to help build more specific and meaningful connections and invite them to share their personal “why” with one another (and you).
- Make space for whatever they share about their perspectives and experiences, remembering that purpose is universal — but not uniform. Normalize that there is no “right” way to find meaning at work. As conversations unfold, actively listen for what matters most to your employees. You may want to keep notes for yourself on what you learn about each person’s purpose so you can refer back later, especially if you manage a large team.
- Use this information to help make work more personally relevant for each individual. Importantly, after gaining a better understanding of what drives each of your employees, keep that top-of-mind going forward when interacting with them, assigning tasks, and planning growth and development opportunities for them. That way, you’re motivating employees in a tailored and personalized way.
By working from an understanding of what is individually meaningful to each of your team members, showing compassion for their experiences and identities, and using this information to tailor your interactions, work assignments, and development plans for them going forward, you signal support for employee wellbeing and create an environment where employees feel valued, respected, engaged, and eager to contribute — ultimately driving your team and organization forward.
A Closing Word on Purpose in Leadership
Organizations with a focus on purpose in leadership — with managers who help direct reports find meaning in their work and connect their personal values to the organization’s — have a better chance of attracting, engaging, and retaining talent and enabling the enterprise to meet business objectives more effectively.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Equip your people managers with the mindsets and skillsets required for purpose-driven leadership. Partner with us to create a customized learning journey for your leaders using our research-backed modules. Available leadership topics include Authentic Leadership, Collaboration & Teamwork, Emotional Intelligence, Listening to Understand, Psychological Safety, Self-Awareness, Wellbeing, and more.